APHA show a little bit of their hand at last
In March 2022, a peer-reviewed analysis of badger culling data was published in a top veterinary journal. It used all publicly available data. It showed no detectable difference in bovine TB breakdown between badger culled areas and unculled areas since 2013 (1). Now, after a government information black-out following their look at the data up to 2017, the Defra’s Animal and Plant Health Agency (APHA) have at long last posted a pre-print of their own creation looking at their secretly held data up to 2021.
It is not clear why it has taken so long to release this new analysis, a draft of which was presented at a conference in August 2022 (2).
Cynics might say there has been a search for obscure statistical methods to get the results needed to try to show a badger culling has not been a 100% failure. And of course, it supported the pro-cull rationale to hold data secret and keep quiet about any weakness in policy. This served to enable the 2022 and 2023 killings of over 50,000 mostly healthy badgers, planned and executed by the willing and obedient hands of Natural England (3).
The new pre-print, posted 6th September in ‘bioarchive’ (bioRxiv), is by six members of APHA staff. It tries to use an obscure technique: “Difference in Differences analysis evaluates the effects of the Badger Control Policy on Bovine Tuberculosis in England” to look at Bovine TB breakdown incidence (Withdrawn herds: OTFW) between 2009 and 2020 (4). There are many aspects of this new analysis which are problematic, but here are a few of the more obvious.
A new statistical method of analysis – ‘Difference in differences’ (DID)
This is the first time the DID approach has been used in badger cull analyses and it is simply inappropriate. DID compares the changes in outcomes over time between a population that is enrolled in a programme (a group subject to an intervention) and a population that is not (the control group).
The attempt here is to use the same areas in a ‘before and after’ way. There is no clearly defined control group, it is just the fragmented cull areas before they are licensed to cull. The 52 cull areas are surrounded by and influencing each other during a wide range of tightening testing interventions. They are, therefore, not adequately discrete in space and time, breaking a fundamental DID requirement. So not only is this (DID) an unorthodox approach, but it does not follow the basic rules of the unorthodox approach. It is looking a bit desperate already.

Notably, in the period 2016- 2020, pre-cull and cull areas closely juxta position. Pre-cull and cull cattle testing interventions of course influence changes in adjacent pre-cull and cull areas in an irregular and unpredictable manner, via the constant movement of cattle with different testing and control histories. It’s a mess, and surprising that this has been presented as an appropriate statistical method, considering the subject and the epidemiology involved.
Analysis does not distinguish between different causes of disease decline.
Does the analysis decisively link badger culling to decline in bovine TB in cattle? Not at all. Any possible effect of badger culling is confounded with the continuous multi-faceted and complex tightening of cattle testing that took place in an uneven manner over different and irregular time periods. Some of the very important bTB testing controls used, and the timing of their introduction, are incorrectly described and some of the most important ones are not even mentioned.
The Badger Culling Policy invention
There are places in the manuscript where a claim is made for a link to badger culling, ‘The effect of badger culling…’, but then later this is adjusted to ‘However, this data analysis cannot explicitly distinguish…….’ APHA have stated more than once in their recent epidemiology reports that the cattle breakdown data alone are insufficient to show an effect of culling.

Frankly there is no such thing as the ‘Badger Culling Policy’ (BCP) as framed by this report, beyond just killing badgers. It is an invention trying to characterize extensive cattle testing and movement control measures as just a part of the badger culling bolt-on, rolled out six years after testing control measures had been continuously tightened year on year. To pretend the extensive suite of testing and movement control measures is somehow a part of a whole is just a repeat of the ‘all tools in a box’ nonsense and it deceives. True, some of the more essential measures were increased from the first year of badger culling, but most of them were independent of it and ramped up gradually. So trying to pull them apart in a post-facto try-on will not impress the independent scientist, even if an obliging journal prints it, and industry and Defra promote it with their coterie of academic cheerleaders. Badger culling has just been a pointless distraction to cattle surveillance and control measures to address rampant cattle-to-cattle transmission.
So again, no, the analysis is not able to show causation by badger culling of any change in disease, and Defra and APHA’s judgement could be seen ill-judged by trying to convince anyone that this is credible. It is as clumsy as the Chief Vet’s apologies and efforts on Radio 4’s Farming Today in 2022. Defra boss Richard Benyon has been claiming big figures for badger cull benefits for years, but this does not provide any evidence for them.
What is the ‘true burden of disease’?
The new analysis has a surprising and unconventional interpretation of the ‘true burden of the disease’ or disease ‘prevalence’ in a population. It suggests that ‘incidence’ is the better indicator of true burden, which they must surely understand flies against first principles. It is ‘old thinking’ based on the out-dated views of farm vets who claimed that only visibly lesioned cows are infectious. Yes, incidence has been one unit of disease measurement, and it was the unit used by the RBCT to claim a benefit for badger culling. But science has moved on, and this is a strange attempt to live in the past.
The interpretation contrasts with APHA’s reports and understanding of disease controls if you look closely. It contrasts with the conclusions drawn from better comprehension of the SICCT (skin) test sensitivity and specificity, which has been clarified in recent years. Gamma IFyN testing has revealed a very significant reservoir of undetected reactors (diseased animals) in bTB infected herds, pointing towards undisclosed infection in undetected herds too. This ‘hidden’ reservoir in cattle that remains is what really matters for disease understanding and control. The true burden is bigger than the known breakdowns and identified reactors, why else would the disease persist? Both here and in Republic of Ireland where badgers have been relentlessly persecuted and SICCT and Gamma testing has failed for decades.

So why exactly did APHA attempt this clumsy redefinition of the ‘true burden of disease’. Perhaps because it needs to try to defend the original RBCT analysis which by controversial statistical modelling (5), managed to suggest a relationship between incidence and badger culling, having failed to find a relationship with disease prevalence. The effort applied to carry on killing badgers is deeply disturbing.
But wasn’t bovine TB already reducing before badger culling began?
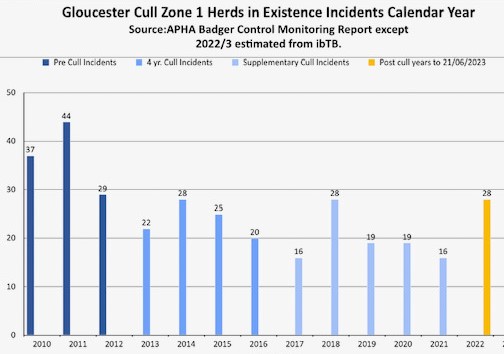
Levels of Bovine TB were falling in many areas soon after annual SICCT testing was introduced in 2010. And well before culling started in most areas. However, the new APHA analysis reduces the analysis of pre-cull data to one data point. This conveniently helps to conceal the significant pre-cull decline and masks the true disease trajectory and results. A logarithmic scale is also used to distort visual effect. Not unlike methods used in the earlier Brunton and Downs reports.
Recent Edge Area data added into the analysis for what purposes?
The new analysis mixes data from 46 High Risk Area study areas with 6 from the Edge Area. These have very different epidemiological and disease control history profiles and the reason for mixing them is not explained. It looks like a deliberate attempt to manipulate the data. Pre-cull gamma testing was intense in the Edge Area. While the manuscript mentions additional gamma testing from 2017, gamma testing was erratic between areas and over time. There were considerable numbers of gamma reactors in many of the cull areas in cull years 1 and 2 of culling with similar disclosures levels to years 3 and 4, but pre-cull use in the HRA was generally low. Mixing them may give you a result you like, but it can be seen through for what it is.

In both HRA and Edge areas, bTB incidence was declining when many of the additional disease control rules were intensified, and badger culling introduced. The addition of this extra data makes it even more impossible to distinguish effects of badger culling and disease control measures that are known to drive down bTB.
Attempt to dismiss peer-reviewed 2022 study published without mentioning it
A comment in the text of the new pre-print says that it is not possible to match badger culled and control areas. This is not only incorrect but unevidenced, with unsubstantiated claims. The 2022 published and peer reviewed study that used this methodology effectively has not been cited. There is no mention of the even more obvious alternative to their complex DID approach, which would be to simply match a series of individual farms in culled and unculled areas. This approach is only available to APHA, which holds all individual farm records confidentially. Such simple monitoring could and should have been an expected outcome of a High Court ruling that required the government to ‘adapt and learn’ from badger culling. Why has it not been done? Perhaps it has been done but gave the wrong results?

Distinct lack of clarity
There is a definite need for clarity in the analysis presented, including the Appendix. This does not seem to be the output from the constrained DID analysis, but something else that is not fully described in the methodology. Analysis uses the lesser known system called STATA (nearly all analysts use R-code). The data is not supplied, and the Stata code is not supplied, so no one can replicate what has been done here. An author, when contacted, said these would be available following publication of the paper. Too late for others to comment on?
Does this draft show that badger culling has reduced bovine TB In cattle?
No, it doesn’t. Because the methods are inappropriate, the results are flawed, and so the conclusions are wrong. There is no way to distinguish between different interventions and change in herd breakdowns since 2013 with the approach taken. Might these results be misleading and deceive if published? Yes. Why has such a flawed analysis been produced now? Is it a try-on to justify Natural England’s new autumn badger blood-fest? Will Defra contractors, grant recipients and a friendly journal whisk it through peer review with recommended friendly reviewers? Probably.
A consultation on culling all badgers over wide areas is being cooked up despite previous policy promises. One could speculate that APHA have been told both by bosses and lawyers that they need to produce evidence that the culling policy has not been a complete waste of life, public funds, and other resources including masses of police time. They are desperate to do this, and get it out right in front of the move to ‘carry on culling’. This preprint aims to be the new truth about badger culling, but it’s all smoke and mirrors.
References
- Langton TES, Jones MW, McGill I. Analysis of the impact of badger culling on bovine tuberculosis in cattle in the high-risk area of England, 2009–2020. Vet Rec 2022; doi:10.1002/vetr.1384
- DEFRA called out over flawed bovine TB claims at international vet conference
- Bovine TB and Badgers: a weakened link
- PREPRINT: Colin P.D. Birch, Mayur Bakrania, Alison Prosser, Dan Brown, Susan M. Withenshaw, Sara H. Downs Difference in Differences analysis evaluates the effects of the Badger Control Policy on Bovine Tuberculosis in England. bioRxiv 2023.09.04.556191; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.04.556191
- PREPRINT: Paul Torgerson, Sonja Hartnack, Philipp Rasmusen et al. Absence of effects of widespread badger culling on tuberculosis in cattle, 13 December 2022, (Version 2) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2362912/v2]